5G IP platform for enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB)
CEVA, the leading licensor of signal processing platforms and artificial intelligence processors for smarter, connected devices, has introduced PentaG, a comprehensive 5G intellectual property (IP) platform for enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB). Compliant to the 3GPP 5G New Radio (NR) Release-15 and software upgradable for Release-16, PentaG is targeted at smartphones, fixed wireless access and the many other embedded devices that can take advantage of multi-gigabit data rates to enable services and use cases such as 4K video streaming, augmented reality, virtual reality, autonomous driving and home broadband.
PentaG builds on CEVA’s two decades of experience in developing DSP platforms for 2G, 3G and 4G LTE modem design, which have been licensed and deployed by many of the world’s leading wireless communications semiconductor companies and smartphone OEMs. To date, more than eight billion handsets have shipped worldwide powered by CEVA DSPs.
Mike Demler, senior analyst at the Linley Group commented: “5G promises to revolutionize how the world communicates, delivering unprecedented levels of performance, coverage and reliability. CEVA’s PentaG modular design offers an innovative approach to handle the complexities of 5G processing for enhanced mobile broadband, combining function-specific IPs together with the latest machine learning techniques in a compelling platform offering.”
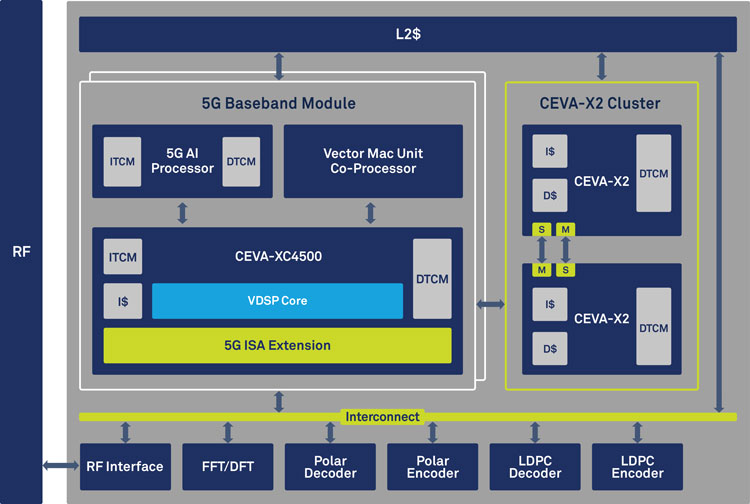
To address the massive performance and technical challenges associated with 5G processing and deliver a comprehensive solution for its customers, PentaG was designed as CEVA’s most advanced set of technologies ever for a baseband architecture. It includes a unique combination of specialized scalar and vector DSP processors with an enhanced 5G Instruction Set Architecture (ISA), specialized co-processors, accelerators, software and other essential IP blocks, in a highly configurable and modular architecture. Included in PentaG is an innovative AI processor that takes advantage of machine learning techniques to deliver up to 8X performance improvement for link adaptation workloads, compared to the conventional software approach. In addition, due to the array of specialized co-processors and accelerators, such as Vector MAC Unit (VMU), PentaG achieves up to 50% power savings for commonly used workloads, all within the low latency constraints and extreme throughput requirements of 5G NR.
Michael Boukaya, vice president and general manager of the wireless business unit at CEVA, commented: “The 5G standard poses immense challenges for wireless semiconductor designers to build modems that are powerful, yet efficient enough to meet the strict power budget constraints of enhanced mobile broadband. We designed PentaG to overcome the limitations of conventional DSP-based LTE/LTE-Advanced architectures, which simply do not scale to support 5G. The PentaG platform is powerful enough to support the most critical 5G NR functions in the most efficient manner possible, while offering the flexibility to allow customers to combine specific PentaG components with their incumbent technologies.”

PentaG supports the full gamut of 5G eMBB use cases, including standalone (SA) and non-standalone (NSA), mmWave and sub-6GHz. The platform sustains an impressive bit-rate of up to ten Gbps and offers a scalable architecture to support most advanced wireless technologies like Massive-MIMO, beamforming and complex link adaptation schemes.
The PentaG platform is composed of a number of specialized IP blocks that together form a comprehensive system to solve complex modem problems. These include:
- Enhanced CEVA-XC4500 DSP with 5G ISA Extensions: based on the silicon-proven CEVA-XC4500 DSP, this enhanced implementation includes new 5G ISA extensions specifically designed to accelerate key functions in the modem. These ISA extensions ensure that the enhanced CEVA-XC4500 delivers a four times performance boost over the existing CEVA-XC4500 in downlink channel modules in the New Radio Physical Downlink Control Channel (NR-PDCCH) and New Radio Physical Downlink Shared Channel (NR-PDSCH) in addition to measurement procedures and link adaptation functions.
- 5G AI Processor: a fully programmable and scalable processor that uses machine learning methods to enable advanced beamforming techniques and link adaptation scenarios as defined in 5G-NR Release15, Type-I and Type-II, using neural networks rather than a traditional database search approach. The 5G AI processor increases downlink data throughput by 20% and ensures unmatched performance under the most advanced Maximum Likelihood Decoding (MLD) equalization schemes.
- Vector MAC Unit (VMU): a fully-programmable co-processor incorporating 64-MAC units, designed to handle advanced channel estimation measurements and schemes in multiple channels including NR-PDSCH and Channel State Information Reference Signal (CSI-RS).
- Cluster of CEVA-X2 DSPs: 5G PHY control is extremely performance intensive and demands ultra-low latency. Utilizing a multi-core cluster composed of CEVA-X2 scalar DSPs with dedicated SoC mechanisms, PentaG offers outstanding PHY control performance.
- Polar and LDPC Encoder and Decoder accelerators: 5G NR eMBB channel coding demands high throughput and very low latency. The Polar and LDPC accelerators are highly tuned to these requirements, ensuring exceptional performance for such compute intensive tasks.
PentaG reduces the enormous complexity of designing next-gen 5G NR enhanced mobile broadband modems. The platform is complemented with a complete hardware and software development environment, including FPGA-based development board, allowing customers to immediately begin their 5G software implementation and accelerate their modem development.
Additionally, customers can take advantage of the PentaG modular architecture to combine their incumbent technologies together with PentaG components for differentiated design and fast time-to-market. CEVA offers the option to license the full PentaG platform or its individual components, which can be integrated into their modem design via standard interfaces.

