Astronauts use a load plate to install the extravehicular experimental load in the space station. The loading happens in a hazardous environment. In a research paper recently published in Space: Science & Technology, Dr. Sun from the School of Mechatronical Engineering, Beijing Institute of Technology, proposed using an autonomous assembly method of the load plate to solve the challenges.
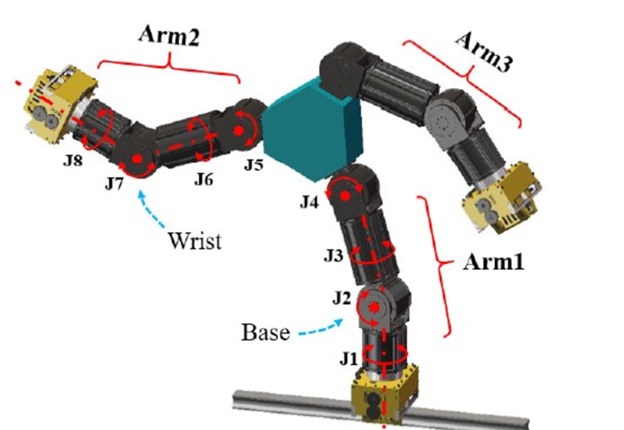
The researchers introduced the concept of a robot with three uniformly distributed 4-DOF arms featuring a 3-DOF wrist joint and a 1-DOF elbow, totally 3×4=12 DOFs. Each arm has a gripper for movement and operation, a monocular vision camera, and a 6-dimensional F/T sensor. They also suggested a method for humanoid dexterous operation of the robot, pose estimations, and autonomous operation control.
At the heart of the research are safety and robot robustness. For more details, visit the Space, Science & Technology Journal article.
